American religion statistics
Latest revision as of 15:42, 19 December 2010
Contents |
2008 ARIS Survey
The Catholic population of the United States has shifted away from the Northeast and towards the Southwest, while secularity continues to grow in strength in all regions of the country, according to a new study conducted by the Program on Public Values at Trinity College. "The decline of Catholicism in the Northeast is nothing short of stunning," said Barry Kosmin, a principal investigator for the American Religious Identification Survey (ARIS). "Thanks to immigration and natural increase among Latinos, California now has a higher proportion of Catholics than New England."
Conducted between February and November of 2008, ARIS 2008 is the third in a landmark series of large, nationally representative surveys of U.S. adults in the 48 contiguous states conducted by Kosmin and Ariela Keysar. Employing the same research methodology as the 1990 and 2001 surveys, ARIS 2008 questioned 54,461 adults in either English or Spanish. With a margin of error of less than 0.5 percent, it provides the only complete portrait of how contemporary Americans identify themselves religiously, and how that self-identification has changed over the past generation.
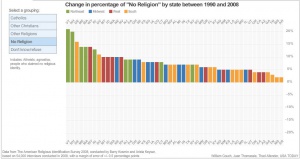
In broad terms, ARIS 2008 found a consolidation and strengthening of shifts signaled in the 2001 survey. The percentage of Americans claiming no religion, which jumped from 8.2 in 1990 to 14.2 in 2001, has now increased to 15 percent. Given the estimated growth of the American adult population since the last census from 207 million to 228 million, that reflects an additional 4.7 million "Nones." Northern New England has now taken over from the Pacific Northwest as the least religious section of the country, with Vermont, at 34 percent "Nones," leading all other states by a full 9 points.
The percentage of Christians in America, which declined in the 1990s from 86.2 percent to 76.7 percent, has now edged down to 76 percent. Ninety percent of the decline comes from the non-Catholic segment of the Christian population, largely from the mainline denominations, including Methodists, Lutherans, Presbyterians, Episcopalians/Anglicans, and the United Church of Christ. These groups, whose proportion of the American population shrank from 18.7 percent in 1990 to 17.2 percent in 2001, all experienced sharp numerical declines this decade and now constitute just 12.9 percent.
Most of the growth in the Christian population occurred among those who would identify only as "Christian," "Evangelical/Born Again," or "non-denominational Christian." The last of these, associated with the growth of megachurches, has increased from less than 200,000 in 1990 to 2.5 million in 2001 to over 8 million today. These groups grew from 5 percent of the population in 1990 to 8.5 percent in 2001 to 11.8 percent in 2008. Significantly, 38.6 percent of mainline Protestants now also identify themselves as evangelical or born again.
"It looks like the two-party system of American Protestantism--mainline versus evangelical--is collapsing," said Mark Silk, director of the Public Values Program. "A generic form of evangelicalism is emerging as the normative form of non-Catholic Christianity in the United State s."
Other key findings:
- Baptists, who constitute the largest non-Catholic Christian tradition, have increased their numbers by two million since 2001, but continue to decline as a proportion of the population.
- Mormons have increased in numbers enough to hold their own proportionally, at 1.4 percent of the population.
- The Muslim proportion of the population continues to grow, from .3 percent in 1990 to .5 percent in 2001 to .6 percent in 2008.
- The number of adherents of Eastern Religions, which more than doubled in the 1990s, has declined slightly, from just over two million to just under. Asian Americans are substantially more likely to indicate no religious identity than other racial or ethnic groups.
- Those who identify religiously as Jews continue to decline numerically, from 3.1 million in 1990 to 2.8 million in 2001 to 2.7 million in 2008--1.2 percent of the population. Defined to include those who identify as Jews by ethnicity alone, the American Jewish population has remained stable over the past two decades.
- Only 1.6 percent of Americans call themselves atheist or agnostic. But based on stated beliefs, 12 percent are atheist (no God) or agnostic (unsure), while 12 percent more are deistic (believe in a higher power but not a personal God). The number of outright atheists has nearly doubled since 2001, from 900 thousand to 1.6 million. Twenty-seven percent of Americans do not expect a religious funeral at their death.
- Adherents of New Religious movements, inc luding Wiccans and self-described pagans, have grown faster this decade than in the 1990s.[1]
Highlights
The ARIS 2008 survey was carried out during February-November 2008 and collected answers from 54,461 respondents who were questioned in English or Spanish.
- The American population self-identifies as
predominantly Christian but Americans are slowly becoming less Christian.
- 86% of American adults identified as
Christians in 1990 and 76% in 2008.
- The historic Mainline churches and
denominations have experienced the steepest declines while the non- denominational Christian identity has been trending upward particularly since 2001.
- The challenge to Christianity in
the U.S. does not come from other religions but rather from a rejection of all forms of organized religion.
- 34% of American adults considered
themselves "Born Again or Evangelical Christians" in 2008.
- The U. S. population continues to show
signs of becoming less religious, with one out of every five Americans failing to indicate a religious identity in 2008.
- The "Nones" (no stated religious
preference, atheist, or agnostic) continue to grow, though at a much slower pace than in the 1990s, from 8.2% in 1990, to 14.1% in 2001, to 15.0% in 2008.
- Asian Americans are substantially
more likely to indicate no religious identity than other racial or ethnic groups.
- One sign of the lack of attachment of
Americans to religion is that 27% do not expect a religious funeral at their death.
- Based on their stated beliefs rather than
their religious identification in 2008, 70% of Americans believe in a personal God, roughly 12% of Americans are atheist (no God) or agnostic (unknowable or unsure), and another 12% are deistic (a higher power but no personal God).
- America's religious geography has been
transformed since 1990. Religious switching along with Hispanic immigration has significantly changed the religious profile of some states and regions. Between 1990 and 2008, the Catholic population proportion of the New England states fell from 50% to 36% and in New York it fell from 44% to 37%, while it rose in California from 29% to 37% and in Texas from 23% to 32%.
Overall the 1990-2008 ARIS time series shows that changes in religious self-identification in the first decade of the 21st century have been moderate in comparison to the 1990s, which was a period of significant shifts in the religious composition of the United States.
2007
An extensive new survey by the Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life details statistics on religion in America and explores the shifts taking place in the U.S. religious landscape. Based on interviews with more than 35,000 Americans age 18 and older, the U.S. Religious Landscape Survey finds that religious affiliation in the U.S. is both very diverse and extremely fluid. Key Findings and Statistics on Religion in America
More than one-quarter of American adults (28%) have left the faith in which they were raised in favor of another religion - or no religion at all. If change in affiliation from one type of Protestantism to another is included, 44% of adults have either switched religious affiliation, moved from being unaffiliated with any religion to being affiliated with a particular faith, or dropped any connection to a specific religious tradition altogether.
The survey finds that the number of people who say they are unaffiliated with any particular faith today (16.1%) is more than double the number who say they were not affiliated with any particular religion as children. Among Americans ages 18-29, one-in-four say they are not currently affiliated with any particular religion.
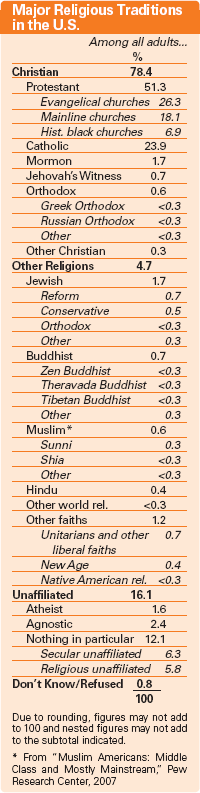
The Landscape Survey confirms that the United States is on the verge of becoming a minority Protestant country; the number of Americans who report that they are members of Protestant denominations now stands at barely 51%. Moreover, the Protestant population is characterized by significant internal diversity and fragmentation, encompassing hundreds of different denominations loosely grouped around three fairly distinct religious traditions - evangelical Protestant churches (26.3% of the overall adult population), mainline Protestant churches (18.1%) and historically black Protestant churches (6.9%).
While those Americans who are unaffiliated with any particular religion have seen the greatest growth in numbers as a result of changes in affiliation, Catholicism has experienced the greatest net losses as a result of affiliation changes. While nearly one-in-three Americans (31%) were raised in the Catholic faith, today fewer than one-in-four (24%) describe themselves as Catholic. These losses would have been even more pronounced were it not for the offsetting impact of immigration. The Landscape Survey finds that among the foreign-born adult population, Catholics outnumber Protestants by nearly a two-to-one margin (46% Catholic vs. 24% Protestant); among native-born Americans, on the other hand, the statistics show that Protestants outnumber Catholics by an even larger margin (55% Protestant vs. 21% Catholic). Immigrants are also disproportionately represented among several world religions in the U.S., including Islam, Hinduism and Buddhism.
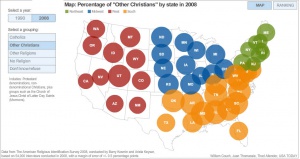
Although there are about half as many Catholics in the U.S. as Protestants, the number of Catholics nearly rivals the number of members of evangelical Protestant churches and far exceeds the number of members of both mainline Protestant churches and historically black Protestant churches. The U.S. also includes a significant number of members of the third major branch of global Christianity - Orthodoxy - whose adherents now account for 0.6% of the U.S. adult population. American Christianity also includes sizeable numbers of Mormons (1.7% of the adult population), Jehovah's Witnesses (0.7%) and other Christian groups (0.3%).
Like the other major groups, people who are unaffiliated with any particular religion (16.1%) also exhibit remarkable internal diversity. Although one-quarter of this group consists of those who describe themselves as either atheist or agnostic (1.6% and 2.4% of the adult population overall, respectively), the majority of the unaffiliated population (12.1% of the adult population overall) is made up of people who simply describe their religion as "nothing in particular." This group, in turn, is fairly evenly divided between the "secular unaffiliated," that is, those who say that religion is not important in their lives (6.3% of the adult population), and the "religious unaffiliated," that is, those who say that religion is either somewhat important or very important in their lives (5.8% of the overall adult population).
Even smaller religions in the U.S. reflect considerable internal diversity. For instance, most Jews (1.7% of the overall adult population) identify with one of three major groups: Reform, Conservative or Orthodox Judaism. Similarly, more than half of Buddhists (0.7% of the overall adult population) belong to one of three major groups within Buddhism: Zen, Theravada or Tibetan Buddhism. Muslims (0.6% of the overall adult population) divide primarily into two major groups: Sunni and Shia. A Very Competitive Religious Marketplace A Note on Defining Religious Affiliation
The survey finds that constant movement characterizes the American religious marketplace, as every major religious group is simultaneously gaining and losing adherents. Those that are growing as a result of religious change are simply gaining new members at a faster rate than they are losing members. Conversely, those that are declining in number because of religious change simply are not attracting enough new members to offset the number of adherents who are leaving those particular faiths.
To illustrate this point, one need only look at the biggest gainer in this religious competition - the unaffiliated group. People moving into the unaffiliated category outnumber those moving out of the unaffiliated group by more than a three-to-one margin. At the same time, however, a substantial number of people (nearly 4% of the overall adult population) say that as children they were unaffiliated with any particular religion but have since come to identify with a religious group. This means that more than half of people who were unaffiliated with any particular religion as a child now say that they are associated with a religious group. In short, the Landscape Survey shows that the unaffiliated population has grown despite having one of the lowest retention rates of all "religious" groups.
Another example of the dynamism of the American religious scene is the experience of the Catholic Church. Other surveys - such as the General Social Surveys, conducted by the National Opinion Research Center at the University of Chicago since 1972 - find that the Catholic share of the U.S. adult population has held fairly steady in recent decades at around 25%. What this apparent stability obscures, however, is the large number of people who have left the Catholic Church. Approximately one-third of the survey respondents who say they were raised Catholic no longer describe themselves as Catholic. This means that roughly 10% of all Americans are former Catholics. These losses, however, have been partly offset by the number of people who have changed their affiliation to Catholicism (2.6% of the adult population) but more importantly by the disproportionately high number of Catholics among immigrants to the U.S. The result is that the overall percentage of the population that identifies as Catholic has remained fairly stable.
In addition to detailing the current religious makeup of the U.S. and describing the dynamic changes in religious affiliation, the findings from the Landscape Survey also provide important clues about the future direction of religious affiliation in the U.S. By detailing the age distribution of different religious groups, for instance, the study's statistics on religion show that more than six-in-ten Americans age 70 and older (62%) are Protestant but that this number is only about four-in-ten (43%) among Americans ages 18-29. Conversely, young adults ages 18-29 are much more likely than those age 70 and older to say that they are not affiliated with any particular religion (25% vs. 8%). If these generational patterns persist, recent declines in the number of Protestants and growth in the size of the unaffiliated population may continue.
Major changes in the makeup of American Catholicism also loom on the horizon. Latinos, who already account for roughly one-in-three adult Catholics overall, may account for an even larger share of U.S. Catholics in the future. For while Latinos represent roughly one-in-eight U.S. Catholics age 70 and older (12%), they account for nearly half of all Catholics ages 18-29 (45%).
Finally, the Landscape Survey documents how immigration is adding even more diversity to the American religious quilt. For example, Muslims, roughly two-thirds of whom are immigrants, now account for roughly 0.6% of the U.S. adult population; and Hindus, more than eight-in-ten of whom are foreign born, now account for approximately 0.4% of the population. Other Survey Highlights
Other highlights in the report include
- Men are significantly more likely than women to claim no religious affiliation. Nearly one-in-five men say they have no formal religious affiliation, compared with roughly 13% of women.
- Among people who are married, nearly four-in-ten (37%) are married to a spouse with a different religious affiliation. (This figure includes Protestants who are married to another Protestant from a different denominational family, such as a Baptist who is married to a Methodist.) Hindus and Mormons are the most likely to be married (78% and 71%, respectively) and to be married to someone of the same religion (90% and 83%, respectively).
- Mormons and Muslims are the groups with the largest families; more than one-in-five Mormon adults and 15% of Muslim adults in the U.S. have three or more children living at home.
- The Midwest most closely resembles the religious makeup of the overall population. The South, by a wide margin, has the heaviest concentration of members of evangelical Protestant churches. The Northeast has the greatest concentration of Catholics, and the West has the largest proportion of unaffiliated people, including the largest proportion of atheists and agnostics.
- Of all the major racial and ethnic groups in the United States, black Americans are the most likely to report a formal religious affiliation. Even among those blacks who are unaffiliated, three-in-four belong to the "religious unaffiliated" category (that is, they say that religion is either somewhat or very important in their lives), compared with slightly more than one-third of the unaffiliated population overall.
- Nearly half of Hindus in the U.S., one-third of Jews and a quarter of Buddhists have obtained post-graduate education, compared with only about one-in-ten of the adult population overall. Hindus and Jews are also much more likely than other groups to report high income levels.
- People not affiliated with any particular religion stand out for their relative youth compared with other religious traditions. Among the unaffiliated, 31% are under age 30 and 71% are under age 50. Comparable numbers for the overall adult population are 20% and 59%, respectively.
- By contrast, members of mainline Protestant churches and Jews are older, on average, than members of other groups. Roughly half of Jews and members of mainline churches are age 50 and older, compared with approximately four-in-ten American adults overall.
- In sharp contrast to Islam and Hinduism, Buddhism in the U.S. is primarily made up of native-born adherents, whites and converts. Only one-in-three American Buddhists describe their race as Asian, while nearly three-in-four Buddhists say they are converts to Buddhism.
- Jehovah's Witnesses have the lowest retention rate of any religious tradition. Only 37% of all those who say they were raised as Jehovah's Witnesses still identify themselves as Jehovah's Witnesses.
- Members of Baptist churches account for one-third of all Protestants and close to one-fifth of the total U.S. adult population. Baptists also account for nearly two-thirds of members of historically black Protestant churches.
About the Survey
These are some of the key findings of the Pew Forum's U.S. Religious Landscape Survey, which draws primarily on a new nationwide survey conducted from May 8 to Aug. 13, 2007, among a representative sample of more than 35,000 adults in the U.S., with additional over-samples of Eastern Orthodox Christians, Buddhists and Hindus. The study also takes advantage of the 2007 survey of American Muslims ("Muslim Americans: Middle Class and Mostly Mainstream"), which was conducted by the Forum in partnership with its sister projects, the Pew Research Center for the People & the Press, the Pew Hispanic Center and the Pew Global Attitudes Project. In total, these surveys included interviews with more than 36,000 Americans.
References
See also
- Source: http://religions.pewforum.org/reports/detailed_tables" rel="nofollow" title="">http://religions.pewforum.org/reports/detailed_tables
This site costs a lot of money in bandwidth and resources. We are glad to bring it to you free, but would you consider helping support our site by making a donation? Any amount would go a long way towards helping us continue to provide this useful service to the community.
Click on the Paypal button below to donate. Your support is most appreciated! |
|---|