Pagan holidays
Most modern day celebrations have their roots in Pagan seasonal celebrations.
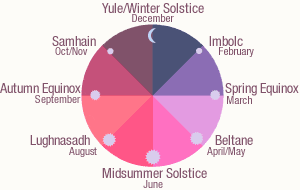
The Pagan seasonal cycle is often called the Wheel of the Year. Almost all Pagans celebrate a cycle of eight festivals, which are spaced every six or seven weeks through the year and divide the wheel into eight segments. Wheel with eight segments representing the subdivision of the year
Four of the festivals have Celtic origins and are known by their Celtic names, Imbolc, Beltane, Lughnasadh and Samhain.
The other four are points in the solar calendar. These are Spring and Autumn Equinox (when the length of the day is exactly equal to the night), Summer and Winter Solstice (longest and shortest days of the year). Neolithic sites such as Stonehenge act as gigantic solar calendars which marked the solstices and equinoxes and show that solar festivals have been significant dates for hundreds of thousands of years.
(The seasonal differences between the hemispheres mean solar festivals are celebrated opposite different dates in the southern hemisphere.)
Contents |
Imbolc
Imbolc (pronounced 'im'olk' also known as Oimelc) comes from an Irish word that was originally thought to mean 'in the belly' although many people translate it as 'ewe's milk' (oi-melc).
Imbolc was one of the cornerstones of the Celtic calendar. For them the success of the new farming season was of great importance. As winter stores of food were getting low Imbolc rituals were performed to harness divine energy that would ensure a steady supply of food until the harvest six months later.
Like many Celtic festivals, the Imbolc celebrations centred around the lighting of fires. Fire was perhaps more important for this festival than others as it was also the holy day of Brigid (also known as Bride, Brigit, Brid), the Goddess of fire, healing and fertility. The lighting of fires celebrated the increasing power of the Sun over the coming months. For the Christian calendar, this holiday was reformed and renamed 'Candlemas' when candles are lit to remember the purification of the Virgin Mary.
Imbolc is still a special time for Pagans. As people who are deeply aware of what is going on in the natural world they recognise that there is strength in cold as well as heat, death as well as life. The Horned God reigns over the Autumn and Winter and and although the light and warmth of the world my be weak he is still in his power.
Many feel that human actions are best when they reflect the actions of nature, so as the world slowly springs back into action it is time for the small tasks that are neglected through the busy year. Rituals and activities might include the making of candles, planting spring flowers, reading poetry and telling stories.
Spring equinox
Spring Equinox celebrates the renewed life of the Earth that comes with the Spring. It is a solar festival, celebrated when the length of the day and the night are equal (this happens twice a year, at Spring and Autumn Equinox).
This turn in the seasons has been celebrated by cultures throughout history who held festivals for their gods and goddesses at this time of year. Aphrodite from Cyprus, Hathor from Egypt and Ostara of Scandinavia. The Celts continued the tradition with festivities at this time of year.
Today, Pagans continue to celebrate the coming of Spring. They attribute the changes that are going on in the world to an increase in the powers of their God and Goddess (the personifications of the great force that is at work in the world). At the time of Spring Equinox the God and the Goddess are ofter portrayed as The Green Man and Mother Earth. The Green Man is said to be born of Mother Earth in the depths of winter and to live through the rest of the year until he dies at Samhain.
To celebrate Spring Equinox some Pagans carry out particular rituals. For instance a woman and a man are chosen to act out the roles of Spring God and Goddess, playing out courtship and symbolically planting seeds. Egg races, egg hunts, egg eating and egg painting are also traditional activities at this time of year.
Beltane
Beltane is a Celtic word which means 'fires of Bel' (Bel was a Celtic deity). It is a fire festival that celebrates of the coming of summer and the fertility of the coming year.
Celtic festivals often tied in with the needs of the community. In spring time, at the beginning of the farming calendar, everybody would be hoping for a fruitful year for their families and fields.
Beltane rituals would often include courting: for example, young men and women collecting blossoms in the woods and lighting fires in the evening. These rituals would often lead to matches and marriages, either immediately in the coming summer or autumn.
Other festivities involved fire which was thought to cleanse, purify and increase fertility. Cattle were often passed between two fires and the properties of the flame and the smoke were seen to ensure the fertility of the herd.
Today Pagans believe that at Beltane the God (to whom the Goddess gave birth at the Winter Solstice) achieves the strength and maturity to court and become lover to the Goddess. So although what happens in the fields has lost its significance for most Pagans today, the creation of fertility is still an important issue.
Emma Restall Orr, a modern day Druid, speaks of the 'fertility of our personal creativity'. (Spirits of the Sacred Grove, pub. Thorsons, 1998, pg.110). She is referring to the need for active and creative lives. We need fertile minds for our work, our families and our interests.
Fire is still the most important element of most Beltane celebrations and there are many traditions associated with it. It is seen to have purifying qualities which cleanse and revitalize. People leap over the Beltane fire to bring good fortune, fertility (of mind, body and spirit) and happiness through the coming year.
Although Beltane is the most overtly sexual festival, Pagans rarely use sex in their rituals although rituals often imply sex and fertility. The tradition of dancing round the maypole contains sexual imagary and is still very popular with modern Pagans.
Summer solstice
Solstice, Midsummer or Litha means a stopping or standing still of the sun. It is the longest day of the year and the time when the sun is at its maximum elevation.
This date has had spiritual significance for thousands of years as humans have been amazed by the great power of the sun. The Celts celebrated with bonfires that would add to the sun's energy, Christians placed the feast of St John the Baptist towards the end of June and it is also the festival of Li, the Chinese Goddess of light.
Like other religious groups, Pagans are in awe of the incredible strength of the sun and the divine powers that create life. For Pagans this spoke in the Wheel of the Year is a significant point. The Goddess took over the earth from the horned God at the beginning of spring and she is now at the height of her power and fertility. For some Pagans the Summer Solstice marks the marriage of the God and Goddess and see their union as the force that creates the harvest's fruits.
This is a time to celebrate growth and life but for Pagans, who see balance in the world and are deeply aware of the ongoing shifting of the seasons it is also time to acknowledge that the sun will now begin to decline once more towards winter.
When celebrating midsummer Pagans draw on diverse traditions. In England thousands of Pagans and non-Pagans go to places of ancient religious sites such as Stonehenge and Avebury to see the sun rising on the first morning of summer.
Lughnasadh
Lughnasadh (pronouced loo'nass'ah) comes at the beginning of August. It is one of the Pagan festivals of Celtic origin which split the year into four.
Celts held the festival of the Irish god Lugh at this time and later, the Anglo-Saxons marked the festival of hlaefmass - loaf mass or Lammas - at this time.
For these agricultural communities this was the first day of the harvest, when the fields would be glowing with corn and reaping would begin. The harvest period would continue until Samhain when the last stores for the winter months would be put away.
Although farming is not an important part of modern life, Lughnasadh is still seen as a harvest festival by Pagans and symbols connected with the reaping of corn predominate in its rites.
Autumn equinox
Autumn Equinox (also known as Mabon or Harvest Home) is celebrated when day and night are of equal duration before the descent into increasing darkness and is the final festival of the season of harvest.
In nature, the activity of the summer months slows down to the hibernation for the winter. For many Pagans, now is time to reflect on the past season.
It is also a time to recoginze that the balance of the year has changed, the wheel has turned and summer is now over.
Astrologers will recognize this as the date the sun enters the sign of Libra - the Scales of Balance.
This is one of the least celebrated of the Pagan festivals although a harvest festival may be held to thank the Goddess for giving enough food to last the winter.
Samhain
Samhain (pronounced 'sow'inn') is a very important date in the Pagan calendar for it marks the Feast of the Dead. Many Pagans also celebrate it as the old Celtic New Year (although some mark this at Imbolc). It is also celebrated by non-Pagans who call this festival Halloween.
Samhain has been celebrated in Britain for centuries and has its origin in Pagan Celtic traditions. It was the time of year when the veils between this world and the Otherworld were believed to be at their thinnest: when the spirits of the dead could most readily mingle with the living once again. Later, when the festival was adopted by Christians, they celebrated it as All Hallows' Eve, followed by All Saints Day, though it still retained elements of remembering and honoring the dead.
To most modern Pagans, while death is still the central theme of the festival this does not mean it is a morbid event. For Pagans, death is not a thing to be feared. Old age is valued for its wisdom and dying is accepted as a part of life as necessary and welcome as birth. While Pagans, like people of other faiths, always honor and show respect for their dead, this is particularly marked at Samhain. Loved ones who have recently died are remembered and their spirits often invited to join the living in the celebratory feast. It is also a time at which those born during the past year are formally welcomed into the community. As well as feasting, Pagans often celebrate Samahin with traditional games such as bobbing for apples.
Death also symbolizes endings and Samhain is therefore not only a time for reflecting on mortality, but also on the passing of relationships, jobs and other significant changes in life. A time for taking stock of the past and coming to terms with it, in order to move on and look forward to the future.
Winter solstice
The Pagan celebration of Winter Solstice (also known as Yule) is one of the oldest winter celebrations in the world.
Ancient people were hunters and spent most of their time outdoors. The seasons and weather played a very important part in their lives. Because of this many ancient people had a great reverence for, and even worshipped the sun. The Norsemen of Northern Europe saw the sun as a wheel that changed the seasons. It was from the word for this wheel, houl, that the word yule is thought to have come. At mid-winter the Norsemen lit bonfires, told stories and drank sweet ale.
The ancient Romans also held a festival to celebrate the rebirth of the year. Saturnalia ran for seven days from the 17th of December. It was a time when the ordinary rules were turned upside down. Men dressed as women and masters dressed as servants. The festival also involved decorating houses with greenery, lighting candles, holding processions and giving presents.
The Winter Solstice falls on the shortest day of the year (21st December) and was celebrated in Britain long before the arrival of Christianity. The Druids (Celtic priests) would cut the mistletoe that grew on the oak tree and give it as a blessing. Oaks were seen as sacred and the winter fruit of the mistletoe was a symbol of life in the dark winter months.
It was also the Druids who began the tradition of the yule log. The Celts thought that the sun stood still for twelve days in the middle of winter and during this time a log was lit to conquer the darkness, banish evil spirits and bring luck for the coming year.
Many of these customs are still followed today. They have been incorporated into the Christian and secular celebrations of Christmas.
This site costs a lot of money in bandwidth and resources. We are glad to bring it to you free, but would you consider helping support our site by making a donation? Any amount would go a long way towards helping us continue to provide this useful service to the community.
Click on the Paypal button below to donate. Your support is most appreciated! |
|---|